Robotic Process Automation: Your Simplified Guide
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, businesses are embracing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) as a game-changing solution to accelerate the digital transformation journey. With technology at the forefront, business leaders and IT professionals are harnessing the power of automation to streamline their operations, increase efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
RPA is like having a team of super-smart robots that can perform repetitive tasks quickly and with great precision. Imagine having a robot friend who can help you with tasks like entering data, organizing information, and even answering customer inquiries. Sounds cool, right? This is why many business leaders and technology experts are excited about implementing RPA in their organizations.
But what exactly is RPA, and why is it so special? In this guide, we’ll explore how RPA is changing the way businesses operate and how it can make our lives easier. So, get ready for an exciting journey into the world of RPA, where robots and technology come together to make work faster, smarter, and more fun!
Table of contents
What is Robotic Process Automation with example?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a special technology that uses smart robots to help us with our work. It’s like having virtual helpers that can do repetitive tasks for us automatically. You know how we use tools to make tasks easier? Well, RPA is like having digital tools that can do things like entering data or filling out forms without us having to do it ourselves.
Imagine you have a robot friend that can follow specific rules and instructions to get things done. These robots, or bots, are like super-smart computer programs. They can do tasks like copying and pasting information, organizing data, or even answering simple questions.
RPA is all about using these smart robots to make our work quicker and more accurate. By letting robots handle repetitive tasks, we have more time to focus on important and creative work. It’s like having an extra pair of hands to help us with the boring stuff, while we do the fun and important things. RPA is changing the way we work, making it easier and more efficient.
Robotic Process Automation Example:
Imagine you have a favorite online store that sells toys. Every day, they receive many orders from customers who want to buy different toys. Normally, the store employees have to manually type in all the order details, like the customer’s name, address, and the toys they want to buy. It can be a lot of work and take a long time!
But with Robotic Process Automation (RPA), things become much easier and faster! The store can use special computer robots, like super-smart helpers, to do this job. These robots are programmed to read the order information from emails or forms and automatically enter it into the store’s computer system. They follow specific rules, like where to put each piece of information and how to organize it correctly.
So instead of spending a lot of time typing in the orders, the robots can do it very quickly. This helps the store get the orders processed faster and start preparing the toys for delivery. It also reduces mistakes because the robots are very good at following the rules and making sure everything is entered correctly.
Core Components of Robotic Process Automation
Here are the core components of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) explained in a way that a Grade 6 student in the United States can understand:
- Robots: In RPA, robots are like super-smart computer programs or software that can do tasks automatically. These robots are not physical robots like the ones we see in movies, but virtual robots that work inside computers. They can perform tasks on the computer just like we do, but much faster and without getting tired.
- Rules: Just like we have rules to follow in different situations, robots in RPA have their own set of rules. These rules tell the robots what to do and how to do it. It’s like giving them a step-by-step guide to complete their tasks correctly. For example, if a robot is helping with order entry, the rules will tell it where to find the customer’s name, address, and the toys they want to buy.
- Workflows: Workflows are like a series of steps or actions that need to be followed to complete a task. Think of it as a recipe for the robots to follow. Workflows help the robots understand the order in which things need to be done and how to do them correctly. For example, a workflow for a robot helping with order entry may include steps like reading the email, extracting the order details, and entering them into the computer system.
What are the types of Robotic Process Automation?
There are three types of RPA that allow businesses to use robots in different ways to make work easier, faster, and more efficient.
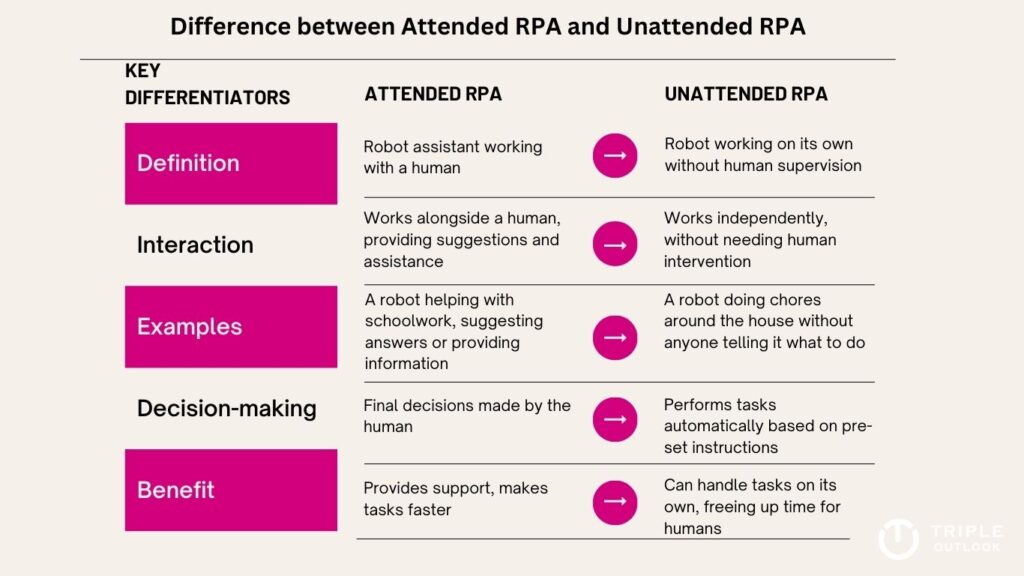
- Attended RPA: Attended RPA is like having a robot assistant that works alongside a human employee. It helps with tasks that require both human judgment and the robot’s help. For example, let’s say a customer service representative needs to answer emails. The robot can suggest responses or provide information to make the job easier, but the final decision is made by the human.
- Unattended RPA: Unattended RPA is like having a robot that works on its own without human supervision. It can handle tasks that are fully automated and don’t need human intervention. For example, a robot can automatically process invoices or generate reports without needing a person to watch over it.
- Hybrid RPA: Hybrid RPA combines both attended and unattended RPA. It means that robots can work independently on some tasks and also collaborate with humans on others. This type of RPA allows for flexibility and efficiency, as humans and robots can work together to get things done.
In addition to Robotic Process Automation (RPA), there are two other exciting technologies that work hand in hand with RPA: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Let’s explore what they mean here.
Introducing the Concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in RPA
Let’s understand the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) first.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Artificial Intelligence, or AI for short, is like giving computers the ability to think and learn just like humans do. It’s like having a brain for a computer! AI helps computers make smart decisions and perform tasks that would usually require human intelligence. It can analyze information, recognize patterns, and even understand human language.
- Machine Learning (ML): Machine Learning is a special part of AI that focuses on teaching computers to learn from experience. It’s like training a computer to become smarter over time. ML algorithms help computers learn from data and make predictions or decisions based on what they have learned. The more data they have, the better they become at solving problems and making accurate choices.
How do AI and ML relate to RPA?
Well, AI and ML can be used in RPA to make robots even smarter and more efficient. They help the robots understand and process information better. For example, imagine a robot that helps with customer service. With AI, it can understand and respond to customer questions in a more human-like way. With ML, it can learn from previous customer interactions to provide better and more personalized assistance.
So, How AI is used in RPA?
AI is like giving computers the ability to think and learn, and it can be really helpful in making RPA even smarter. Here’s how AI is used in RPA:
- AI helps RPA robots understand human language.
- AI enables RPA robots to analyze and extract meaningful information from text.
- AI assists RPA robots in making smart decisions based on data analysis and pattern recognition.
- AI allows RPA robots to learn and improve over time.
- With AI, RPA robots can understand and respond to customer queries in a more human-like way.
- AI helps RPA robots become more efficient and effective in performing tasks.
These points provide a concise overview of how AI is applied in RPA, making robots smarter, more capable, and better equipped to assist humans in various tasks. Let’s discover RPA use cases now.
What are the use cases for RPA?
RPA can be used in various areas of business to make tasks faster, more accurate, and less time-consuming. Here are some typical use cases for RPA:
- Data entry and management: RPA robots can help with entering and managing data. For example, they can input information from forms into a computer system, update databases, or organize data in spreadsheets. This saves time and reduces the chance of errors that can occur when humans do repetitive tasks.
- Invoice processing and accounts payable: RPA robots can assist with processing invoices and managing accounts payable. They can extract relevant information from invoices, match them with purchase orders, and update accounting systems. This helps businesses keep track of their finances efficiently.
- Customer onboarding and support: RPA robots can streamline customer onboarding processes and provide support. They can collect and verify customer information, generate welcome emails, or even answer frequently asked questions. This ensures a smooth and prompt experience for customers.
- HR and employee management: RPA robots can help with HR tasks such as employee onboarding, managing employee data, or processing leave requests. They can automate processes like filling out forms, updating employee records, and sending reminders. This allows HR teams to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Supply chain and inventory management: RPA robots can assist in supply chain and inventory management. They can monitor stock levels, generate purchase orders, and track shipments. By automating these processes, businesses can ensure efficient inventory management and timely deliveries.
- Regulatory compliance and reporting: RPA robots can help with regulatory compliance and reporting tasks. They can gather data, perform checks, and generate reports that comply with legal requirements. This ensures businesses meet their obligations while reducing the risk of human error.
Robots make work faster for businesses. But the question is how to use these robots. Let’s dive in and discover how to implement Robotic Process Automation!
How to implement Robotic Process Automation
Implementing RPA is like teaching a robot to do certain jobs that humans used to do! We will break down the process into simple steps, so you can understand how RPA works and how businesses make it happen. Implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves several steps. Let’s break down the process into simpler terms:
Step 1: Identify tasks for automation
The first step is to identify which tasks or processes can be automated using RPA. These are usually tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and involve a lot of manual work. For example, data entry, invoice processing, or customer support tasks.
Step 2: Design the automation workflow
Once the tasks are identified, the next step is to design the workflow for automation. This means deciding how the RPA robot will perform each step of the task. It’s like creating a step-by-step plan for the robot to follow.
Step 3: Develop the RPA robot
After designing the workflow, the RPA robot needs to be developed. This involves writing the necessary code or configuring the RPA software to perform the desired actions. The robot is like a computer program that follows the instructions you give it.
Step 4: Test and refine
Once the RPA robot is developed, it’s important to test it to ensure it works correctly. This involves running the robot on sample tasks or processes and checking if it performs as expected. If there are any issues or errors, adjustments can be made to refine the robot’s behavior.
Step 5: Implement and monitor
After successful testing, the RPA robot can be implemented into business operations. It starts performing the automated tasks as designed. It’s important to monitor the robot’s performance to ensure it continues to work effectively and make any necessary adjustments along the way.
Step 6: Training and Adoption
To make the implementation successful, employees need to be trained on how to work with the RPA robot. They need to understand how it works, how to interact with it, and how it can assist them in their work. The adoption of RPA requires cooperation and collaboration between humans and robots.
Step 7: Continuous improvement
RPA implementation is an ongoing process. It’s important to monitor and improve the robot’s performance continuously. This can involve gathering feedback from employees, identifying areas for optimization, and making necessary updates or enhancements to the RPA robot.
That’s it! By following these 7 steps, businesses can harness the power of automation and make their work more efficient and productive.
However, there are a few things to keep in mind before you implement RPA in your key business functional areas. Let’s discover them in our next section.
Implementing RPA: Things to Consider
Before a business decides to use Robotic Process Automation (RPA), there are a few important things to think about. These pre-implementation considerations help ensure that RPA is a good fit and brings the desired benefits. Let’s look at these considerations:
- Assessing process suitability for automation: Not all tasks or processes are suitable for automation. It’s important to assess which tasks can be automated effectively using RPA. For example, tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and involve a lot of data entry are often good candidates for automation.
- Defining clear automation objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs): It’s essential to have a clear understanding of what the business wants to achieve with RPA. This means setting specific goals and objectives for the automation process. For instance, the objective could be to reduce processing time, improve accuracy, or increase productivity. Key performance indicators (KPIs) help measure the success of these objectives.
- Evaluating the ROI and cost-effectiveness of RPA implementation: RPA can bring many benefits, but it’s also important to consider the costs and return on investment (ROI). This means analyzing whether the benefits gained from implementing RPA outweigh the costs involved. It’s like comparing the money spent on RPA with the time and money saved as a result of automation.
- Identifying potential challenges and risks: Implementing RPA can have some challenges and risks that need to be identified and addressed. For example, there might be technical issues, data security concerns, or resistance from employees. By identifying these challenges beforehand, businesses can find solutions and plan for a smooth implementation.
So, when a business decides to implement RPA, they need to consider these pre-implementation considerations along with the right tools and technology to help ensure the effective use of RPA in business operations.
Implementing RPA: Selecting the Right RPA Tools and Technology
When it comes to implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA), choosing the right tools and technology is crucial. Let’s explore what that means in simpler terms:
- Overview of popular RPA tools in the market: There are different RPA tools available in the market, like Blue Prism, UiPath, and Automation Anywhere. These tools help businesses build and deploy their RPA robots. Each tool has its own features and strengths, so it’s important to understand what options are available.
- Factors to consider when choosing an RPA solution: When selecting an RPA solution, there are a few important factors to consider. Scalability is one of them, which means the ability of the RPA solution to handle larger volumes of tasks as the business grows. Compatibility is another factor, ensuring that the RPA tool works well with the existing systems and software used by the business. Ease of use is important too, as it should be user-friendly and easy to understand for both developers and users. Security is also a crucial factor to protect sensitive data and ensure that the RPA solution is safe to use.
- Evaluating vendor support and community resources: It’s essential to assess the support provided by the RPA tool vendor. This includes technical assistance, training, and regular updates to the software. Community resources, such as online forums and user groups, can also be valuable as they provide a platform for sharing knowledge and troubleshooting common issues.
By considering these factors, businesses can select the right RPA tools and technology that meet their needs. This ensures a smooth implementation process and sets the foundation for successful automation.
Ensuring Success with Robotic Process Automation
Implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can bring tremendous benefits to businesses, but it’s important to ensure its success. To make the most out of RPA and achieve the desired outcomes, certain considerations and strategies need to be in place. In this section, we will explore key aspects that contribute to the success of RPA implementation. Let’s discover how to ensure success with Robotic Process Automation!
A. Change Management and Stakeholder Engagement:
To ensure a successful implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), it’s important to manage the changes that come along with it and engage with the people involved. Here’s what that entails:
- Communicating the benefits and goals of RPA: It’s crucial to explain to employees and stakeholders how RPA can make their work easier and more efficient. By highlighting the benefits, such as time savings and reduced errors, everyone can understand the positive impact RPA can have on their daily tasks.
- Addressing potential concerns and resistance to change: Change can sometimes be challenging, and some people may have concerns or resistance to adopting RPA. It’s important to listen to their concerns and address them, providing reassurance and showing how RPA can support their work rather than replace it.
- Providing training and support to employees: Proper training is key to the effective adoption of RPA. Employees should receive training on how to work alongside the robots, understand their roles in the new automated processes, and utilize the RPA tools effectively. Ongoing support should also be provided to address any questions or issues that arise.
B. Ensuring Security and Compliance:
When implementing RPA, it’s vital to prioritize security and compliance with data protection regulations. Here’s what businesses need to consider:
- Addressing data privacy and protection concerns: RPA involves handling data, so it’s important to have measures in place to ensure data privacy and protection. This includes encrypting sensitive information, restricting access to authorized personnel, and implementing secure data storage practices.
- Implementing access controls and user authentication: To prevent unauthorized access to the RPA system and data, access controls and user authentication mechanisms should be put in place. This ensures that only authorized individuals can interact with the RPA tools and perform specific actions.
- Complying with relevant industry regulations: Different industries have specific regulations related to data handling and privacy, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It’s important to understand and comply with these regulations to avoid any legal or compliance issues.
C. Monitoring and Measuring RPA Performance:
To ensure the effectiveness of RPA and drive continuous improvement, monitoring and measuring its performance is essential. Here’s how it can be done:
- Setting up monitoring systems: Implement systems to track the performance of the RPA robots. This involves monitoring their activities, identifying any errors or issues, and ensuring they are working as intended.
- Collecting and analyzing relevant data and metrics: Gather data and metrics to assess the performance of RPA. This can include cycle time (how long it takes to complete a task), error rates (how often mistakes occur), and cost savings (how much money is saved through automation). Analyzing this data helps identify areas for improvement and optimization.
- Using analytics and reporting: Leverage analytics and reporting tools to gain insights from the collected data. This allows businesses to generate reports, visualize performance trends, and make data-driven decisions to enhance RPA processes and drive continuous improvement.
By focusing on change management and stakeholder engagement, ensuring security and compliance, and monitoring and measuring RPA performance, businesses can maximize the success of their RPA implementation and realize the benefits of automation.
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the world of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is also evolving. In our next section, we will explore the exciting future trends and developments that are shaping the landscape of RPA.
Top 3 RPA Trends 2023 & Beyond
The field of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-growing demands of businesses. As we look ahead, several key technology trends are shaping the future of RPA, promising to revolutionize how organizations operate. Get ready to glimpse into the future and discover the exciting world of RPA that lies ahead!
Trend #1 Intelligent Automation and Cognitive RPA
The future of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) holds exciting possibilities with the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) capabilities. Here’s what you need to know:
- Exploring AI and ML in RPA: RPA systems are evolving to become smarter by incorporating AI and ML technologies. This enables robots to learn from data, make decisions, and perform more complex tasks. By using AI algorithms, RPA can adapt and improve its performance over time.
- Potential of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision: Imagine robots understanding and interacting with humans just like we do! NLP allows robots to comprehend and respond to human language, making communication more seamless. Computer vision enables robots to see and understand visual information, allowing them to interpret images and videos.
Trend #2 Hyperautomation and Process Mining
The concept of hyperautomation is revolutionizing business processes by taking automation to the next level. Here’s what it entails:
- Understanding Hyperautomation: Hyperautomation combines RPA with other advanced technologies like AI, ML, and process mining. It aims to automate end-to-end processes by integrating various automation tools and leveraging intelligent decision-making capabilities.
- Exploring Process Mining: Process mining techniques analyze business operations to identify automation opportunities. By examining data logs and process flows, businesses can uncover inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas where automation can streamline processes.
Trend #3 RPA in a Digital Workforce:
The future workforce will see a collaboration between human employees and digital workers. Here’s how RPA fits into this digital landscape:
- Collaboration between Humans and Digital Workers: RPA enables humans and robots to work together harmoniously. Digital workers can handle repetitive and rule-based tasks, freeing up humans to focus on more creative and strategic activities. This collaboration enhances overall productivity and efficiency.
- Potential of Attended RPA: Attended RPA refers to robots that work side-by-side with humans, providing real-time support and assistance. These robots can suggest actions, retrieve information, and automate specific parts of tasks, empowering employees to accomplish their work more effectively.
The future of RPA is filled with advancements in intelligent automation, hyperautomation, and the integration of humans and digital workers. As technology continues to evolve, businesses can expect even greater possibilities and efficiencies with Robotic Process Automation.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA boosts productivity, reduces errors, and enhances customer experiences. It combines the power of technology, such as Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, to make robots smarter and more efficient. Businesses need to carefully consider their processes, choose the right tools, and engage employees for successful RPA implementation.
As we look to the future, RPA will continue to evolve, bringing intelligent automation, hyperautomation, and closer collaboration between humans and digital workers. Embracing RPA unlocks a world of possibilities, streamlining operations and driving transformative changes in the business landscape. So, get ready to embrace the power of RPA and embark on a journey towards enhanced efficiency, innovation, and success!